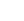CASES OF THE WEEK - “Nuclear Medicine In Sports & Usefulness Of Hybrid Bone Spect-Ct Imaging” by Dr ShekharShikare, Consultant & HOD, Nuclear Medicine, NMC Royal Hospital Sharjah
Nuclear Medicine In Sports & Usefulness Of Hybrid Bone Spect-Ct Imaging (Short Cases- Stress Fractures)
Sports has become a serious profession in the era of advertising and marketing. It is no more a leisure or relaxing activity. Sportsmen are under tremendous pressure from passionate fans and brand sponsors to deliver the best performance, at the highest level of competition. Sportsmen are actively engaged in physical workouts, not to keep themselves physically fit, but rather to enhance their physical stamina and endurance. This vigorous physical activity may at times inflict overuse musculoskeletal injuries on sportsmen, which may risk their professional career at its peak.
Bone stress injuries account for about 10% of the sports medicine practice. Female athletes run three to four times higher risk of bone stress injuries as compared to their male counterparts. Lower extremity bones are most affected (70 – 95%) followed by the spine. The tibia is the most common lower extremity bone reported / known to have stress fractures (50%), followed by the metatarsal, navicular, femur, fibula, and sesamoid bone.
Nuclear Medicine can synergistically contribute to the Sports Medicine field, in the management of sports-related stress injuries. Bone Scintigraphy is commonly requested for evaluation of athletes with pain. Three-Phase Tc-99m MDP Bone Scan along with hybrid SPECT-CT imaging (Hybrid bone SPECT/CT system combines information on abnormal bone metabolism through high contrast-resolution bone SPECT and precise anatomical detail with high spatial resolution of CT) has emerged as the imaging reference standard for diagnosing such injuries.
The inherently high-contrast resolution of the bone scan allows early detection of bone trauma and becomes positive within six to seventy-two hours after the onset of symptoms. The bone scan can demonstrate stress injuries days to weeks before the radiograph. In the initial stages, X-rays may look normal (low sensitivity 15 – 35%) and turn positive in 30 – 70% of the cases on follow-up.
If the X-ray is unremarkable with a clinical suspicion of bone stress injury, then the patient should be subjected to a three-phase bone scan. If a three-phase bone scan is negative, bone pathology (stress injury) is quite unlikely.
The bone scan is known for its high sensitivity equaling that of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. The bone scan, because of its ability of whole-body imaging, detects unsuspected multi-focal trauma or abnormality that is away from the symptomatic site.
Various parameters like intensity and location of tracer uptake and extent of involvement (thickness) of bone, provide useful prognostic information about the severity of the injury, period of inactivity, duration of resumption of rehabilitation, and high risk of developing complications like complete fracture, non-union, or osteonecrosis. Zwas et al. have suggested a classification system for grading the bone stress injuries (Grade I – IV) based on a scintigrapic pattern way back in 1988. Grades I and II injuries are mild grade take a shorter period for healing, and allow an early return to activity, as compared to the higher grade (III and IV) injuries. Location of uptake (injury) involving the tensile aspect (superior) of the femoral neck, anterior cortex of the tibia, and the fifth metatarsals and sesamoid bone are high risk.
Case 1
15 years old boy undergoing mountain climbing and march past training complaining of significant pain in both the knees and left ankle.
X-rays- normal.
99mTc MDP bone scan
Blood pool phase (half body)- focal areas of abnormal pooling of tracer in a) upper medial end of right tibia (hot), b) upper medial end of left tibia (mildly hot), c) lower end of left fibula (hot).
Bone phase (half body)- focal areas of abnormally increased tracer uptakes in a) upper medial end of right tibia (hottest), b) upper medial end of left tibia (mildly hot), c) lower end of left fibula (moderately hot) favors multiple stress fractures (severity wise a > c >b).
Case 2
16 years old boy undergoing heavy exercise and lost around fifteen-kilogram weight in three months. Complaining of severe pain in both the knees and upper leg portions, which is getting worse since last one month.
X-rays- normal.
99mTc MDP bone scan
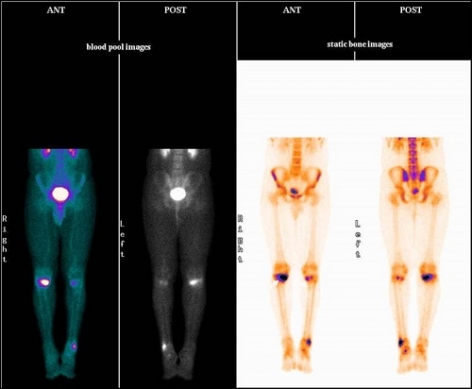
Blood pool phase (half body)- Linear shaped abnormal pooling of tracer seen in proximal third portion of both the tibia (left >right)
Bone phase (half body)- Linear shaped abnormally increased tracer uptakes in proximal third portion of both the tibia (left >right)
favors stress fractures in proximal portion of both the tibial bones.
Case 3
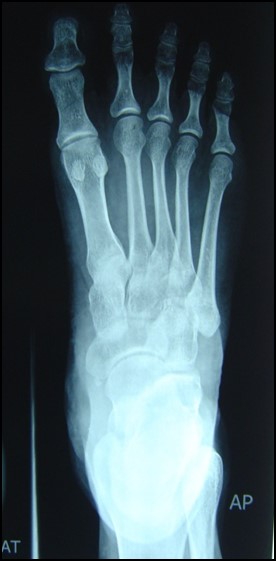
30 years old lady with history of pain in right foot distally since last one month after starting of walking & running. It has started as sudden onset and now become continuous and more with walking.
X-ray right foot twice- WNL
CBC and CRP -WNL
99mTc MDP bone scan
Blood pool phase (foot)- focal area abnormal pooling of tracer seen in 2nd metatarsal bone region of right foot.
Bone phase (foot)- focal area of abnormally increased tracer uptakes seen in 2nd metatarsal bone of right foot, favors stress fracture of 2nd metatarsal bone of right foot distally.
Case 4
27 years lady with history of pain in right ankle region on walking and on movements
Known case of vit D deficiency.
MRI right ankle- focal sprain involving lateral fibers of intermalleolar ligament with minimal focal sprain of the posteior talo-fibular ligament. Minimal focal sprain of tibio-talar component of the deltoid ligaments.
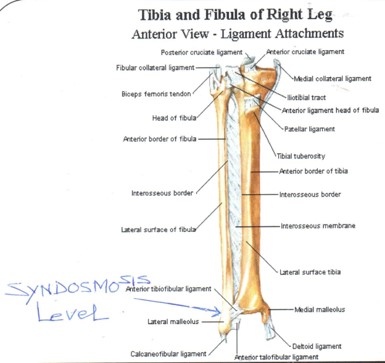
Ref of bone scan with ? Stress fracture distal right fibula at syndosmosis level.
99mTc MDP bone scan
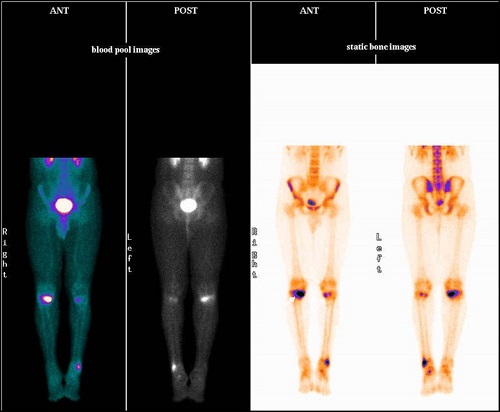
Blood pool phase (half body)- focal areas of abnormal pooling of tracer in a) upper medial end of right tibia (hot), b) upper medial end of left tibia (mildly hot), c) lower end of left fibula (hot).
Bone phase (half body)- focal areas of abnormally increased tracer uptakes in a) upper medial end of right tibia (hottest), b) upper medial end of left tibia (mildly hot), c) lower end of left fibula (moderately hot) favors multiple stress fractures (severity wise a > c >b).
It is recommended that patients with stress-related symptoms be screened utilizing radionuclide bone scintigraphy to facilitate the early detection of abnormalities in bone prior to the development of cortical disruption, thereby preventing increased morbidity and possible disabling sequelae.
Bone imaging in sports medicine.
Journal of Postgraduate Medicine, 01 Jul 1997, 43(3):71-72
STRESS FRACTURES
Case 1
99mTc MDP bone scan
Blood pool phase (half body)- focal areas of abnormal pooling of tracer in a) upper medial end of right tibia (hot), b) upper medial end of left tibia (mildly hot), c) lower end of left fibula (hot).
Bone phase (half body)- focal areas of abnormally increased tracer uptakes in a) upper medial end of right tibia (hottest), b) upper medial end of left tibia (mildly hot), c) lower end of left fibula (moderately hot) favors multiple stress fractures (severity wise a > c >b).
Case 2
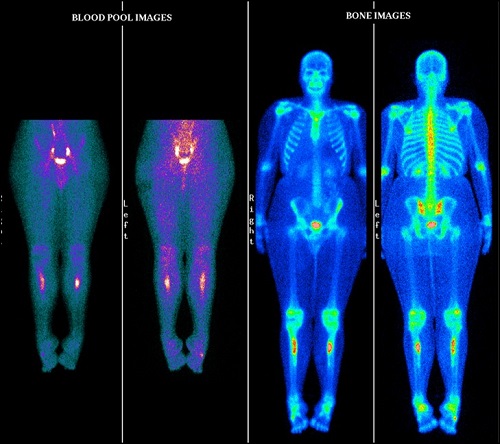
99mTc MDP bone scan
Blood pool phase (half body)- Linear shaped abnormal pooling of tracer seen in proximal third portion of both the tibia (left >right)
Bone phase (half body)- Linear shaped abnormally increased tracer uptakes in proximal third portion of both the tibia (left >right) favors stress fractures in proximal portion of both the tibial bones.
Case 3
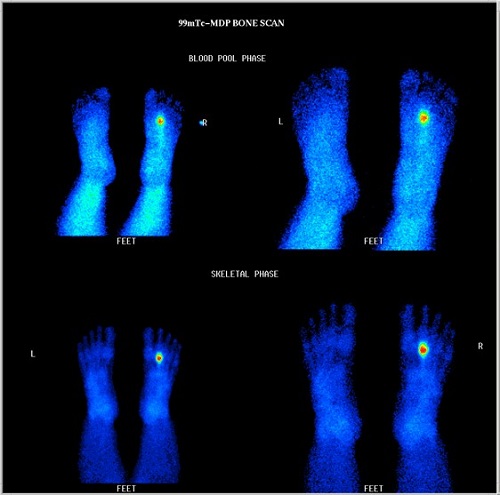
99mTc MDP bone scan
Blood pool phase (foot)- focal area abnormal pooling of tracer seen in 2nd metatarsal bone region of right foot distally.
Bone phase (foot)- focal area of abnormally increased tracer uptakes seen in 2nd metatarsal bone of right foot distally, favors stress fracture of 2nd metatarsal bone of right foot distally.
Case 4
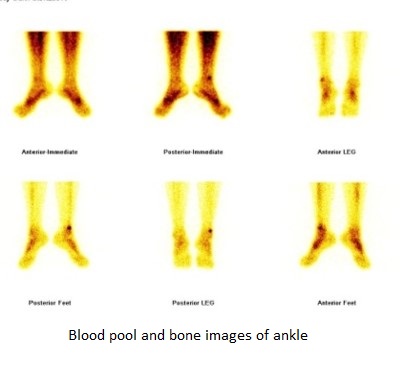
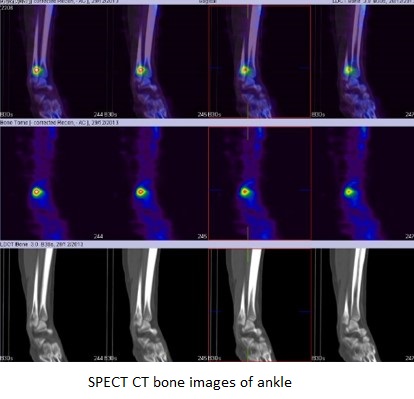
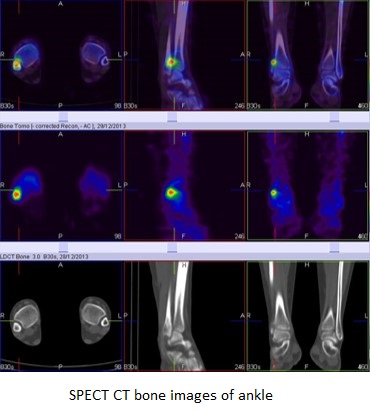
99mTc MDP bone scan
Blood pool phase (ankle)- focal area of abnormal pooling of tracer seen at the lower end of right fibula.
Bone phase (ankle)- focal area of abnormally increased tracer uptakes seen at syndosmosis level of right fibula (Better appreciated in SPECT-CT fused images) favors stress fracture at syndosmosis level of right fibula.