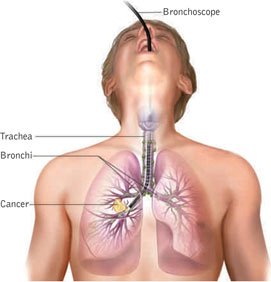
Bronchoscopy
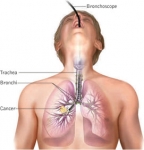
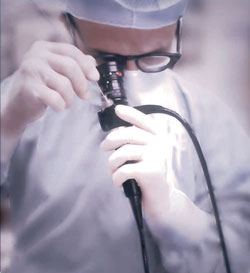
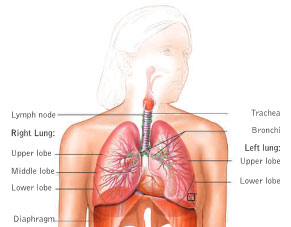
Bronchoscopy is a procedure in which a cylindrical fiber optic scope is inserted in the airways, allowing the physician to visually examine the lower airways including the larynx, trachea, bronchi and bronchioles.
Bronchoscopy may be used for the following purposes:
- To diagnose cancer, tuberculosis, lung infection, or other lung disease
- To examine an inherited deformity of the lungs
- To remove a foreign body in the lungs, such as mucus plug, tumor, or excessive secretions
- To remove tissue samples, also known as biopsy, to test for cancer cells, help with staging the advancement of the lung cancer, or to treat a tumor with laser therapy
- To allow examination of a suspected tumor, obstruction, secretion, bleeding or foreign body in the airways
- To determine the cause of a persistent cough, wheezing, or a cough that includes blood in the sputum
- To evaluate the effectiveness of lung cancer treatments
Preparation
- The doctor should be informed of any allergies and all medications that the patient is currently taking
- The patient should not take medications like Aspirin or anti-inflammatory drugs which interfere with clotting, for a period of time prior to the procedure
- The patient needs to fast for 6 hours prior to the procedure and refrain from drinking any liquids the day of the procedure
- A nurse will ask you to sign a form giving your consent for the procedure and any other steps found necessary during the bronchoscopy
The bronchoscopy takes about 45 to 60 minutes. Prior to bronchoscopy several tests may be done, including chest x-ray and blood works. Sometimes a bronchoscopy is done under general anaesthesia. Patients usually have an intravenous (IV) line in the arm. Most likely the procedure will be done under local anaesthesia, which is sprayed into the nose or mouth. This is necessary to decrease the gag reflex. A sedative may also be used to help the patient relax.
What happens during the procedure?
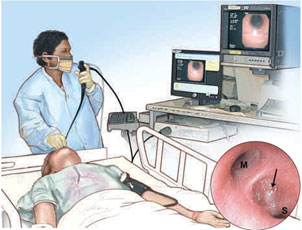
In the bronchoscopy room, you will be monitored. Bronchoscopy assistant or Respiratory therapist will explain the procedure and will assist the doctor with the bronchoscopy. You are encouraged to ask any questions that will help you understand what is about to happen. You will be asked to remove glasses, all jewellery, dentures or other dental appliances. Next you will be given a breathing treatment that contains a local anaesthetic called Xylocaine to numb the airways and make you more comfortable. When the doctor arrives, sedative will be given like Midazolam I.V. to help you relax and sleep. The bronchoscope is guided through your nose and into your lungs by your doctor.
Aftercare
After the bronchoscopy, the patient will be monitored for vital signs such as heartrate, blood pressure, and breathing, while resting in bed. All saliva should be spit into the basin so that it can be examined for the presence of blood. If a biopsy was taken, the patient should not cough or clear the throat as this might dislodge any blood clot that has formed and cause bleeding. No food or drink should be consumed for about 2 hours after the procedure or until the anaesthesia wears off. Diet is gradually progressed. There will also be a temporary sore throat and hoarseness that may last for a few days.
KeyTerms
Anaesthesia - A drug used to loss of sensation. It is used to lessen the pain of surgery and medical procedures.
Bronchi - The network of tubular passages that carry air to the lungs and allow air to be expel led from the lungs.
Bronchioles - Small airways extending from the bronchi into the lobes of the lungs.
Trachea- The windpipe.