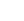Asthma

What is Asthma?
Asthma is a disease of the airways that makes breathing difficult.
Children are more likely to have asthma than adults. Asthma can also start for the first time in adults, and it can be a lasting problem.
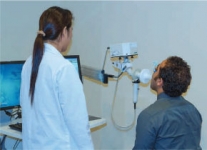
During normal breathing, the bands of muscle that surrounds the airways are relaxed, and air moves freely. In people with asthma the airways tighten and narrow, it become swollen (inflamed) during an attack making it hard for the air to get in and out of the lungs.
There is no cure for asthma, but it can be managed and treated so you can live a normal life.
Symptoms
Wheezing – you may notice a high – pitched whistling sound when you breathe
- Cough – this may be common at night and it can be with or without mucus
- Shortness of breath – a feeling that you cannot get enough air into your lungs.
- Chest tightness or pressure – you may feel that the chest is tight or heavy when breathing
You may not have all of these symptoms or you may have different symptoms at different times. Your symptoms may also vary from one asthma attack to the next, being mild during one attack and severe during another.
Sometimes asthma becomes a life –threatening emergency and it requires immediate emergency care.
Asthma Causes and Triggers
People with asthma have very sensitive airways that react to many different things in the environment called “asthma triggers”. Contact with these triggers cause asthma symptoms to start to worsen.
Common asthma triggers

- Tobacco Smoking or secondhand smoke
- Dust mites
- Pollens
- Molds
- Out door air pollution
- Cockroach Allergen
- Pets ( cat allergy is very important)
Understanding and identifying the things that trigger your asthma will help you manage and control your asthma.
Asthma Diagnosis and Treatment
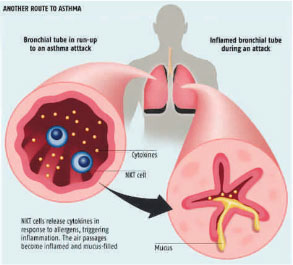
If you suspect that you have asthma see preferably a pulmonologist ( chest specialist), internal medicine and paediatrician can also manage asthma. He or she can examine you and he can request for tests to determine if you have it.
Asthma can be hard to diagnose especially in children. Physical check ups that include checking the lung function test and checking for allergies can help your physician make the right diagnosis.
Spirometry – diagnostic test that measure’s the largest amount of air that you can exhale or breathe out after taking a very deep breath. If you have asthma the spirometry result will be low. Spirometry can measure airflow before and after your asthma medicine, results will confirm diagnosis of asthma. If the spirometry result is normal your doctor might suggest other tests.
Peak Flow Meter – regular peak flow monitoring can help you determine if asthma is controlled or not.
If an asthma diagnosis is made, there are many asthma treatments available to control your asthma. You can control your asthma attack and avoid an attack by taking your medicine exactly the way your healthcare provider tells you to do and by avoiding things that can cause an attack.
Short acting bronchodilators (quick relief)- are often referred to as rescue inhalers and are used to quickly relieve asthma symptoms. They can be used prior to exercise for people who have exercise induced-asthma. If you need to use more often your rescue inhaler then your asthma is not controlled. See your doctor. Using short acting bronchodilators regularly may result in loss of control of asthma management.
Long acting bronchodilators – are used in combination with other asthma medication to control asthma symptoms. Long acting bronchodilators are never used alone as long term therapy for asthma.
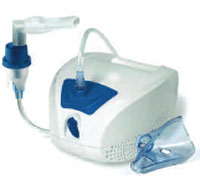
Nebulizer - If you have difficulty using your small inhalers, your doctor may prescribe an asthma nebulizer. Nebulizer with mouthpiece or mask is usually used for infants, small children and older adults or anyone who has difficulty using inhalers with spacers. The nebulizer changes asthma medication from liquid into a mist so that it can be more easily inhaled into the lungs.
Inhaled Steroids – are used to effectively reduce and prevent inflammation and mucus build up in your lungs when your asthma symptoms are persistent with frequent attacks. It must be taken everyday and it is crucially important to use it as directed by your healthcare provider. The benefit of inhaled steroids comes gradually, you will find that your asthma is less troublesome with improve lung function.
The adverse effect of inhaled steroids are very less.
Oral Steroids and IV steroids - are used to treat the inflammation of the breathing tubes in asthmatic patient when there is attack of asthma. Steroids can be taken in tablet form or directly in to the veins ( IV infusion ) in hospitalized patients or in emergency department to relieve asthmatic symptoms . It is a life saving medication in severe asthma attack.
IGE blocker therapy – Omalizumab
It is used for patients with poorly controlled asthma with evidence of specific allergy sensitivity. Omalizumab is used in conjunction with other medication to better control your asthma. It is delivered by subcutaneous injection and should be administered in the clinic or in the hospital. Omalizumab should be given with supervision of pulmonologist.
The medicines prescribed to treat asthma may seem difficult to understand and difficult to use, that’s why it’s important that you work with your healthcare provider on an asthma action plan designed especially for your needs.
References:
- American Lung Association, 2014
http://www.lung.org/lung-disease/asthma/learning-more-about-asthma - American Thoracic Society, 2013
https://www.thoracic.org/patients/index.php