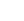CASES OF THE WEEK – “The Hot Spot Hepatbobilairy Scan in Focal Nodular Hyperplasia” by Dr ShekharShikare, HOD & Consultant, Nuclear Medicine
THE HOT SPOT HEPATBOBILAIRY SCAN IN FOCAL NODULAR HYPERPLASIA (SHORT CASE).
Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) is a benign tumor of the liver with an innocuous natural history. It is characterized pathologically by a cholangiolar proliferation associated with hyperplastic hepatocytes, blood vessels and fibrosis. FNH has been studied by various imaging techniques, i.e., ultrasonography (US), computed tomography (CF) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Nuclear medicine tracers, including colloids and hepatobiliary agents, have been proposed for several years as an aid to the diagnosis.
Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) using a hepatobiliary scan with 99mTc Mebrofenin (HIDA). The HIDA uptake was relatively normal in the region of the tumor, but during the clearance phase the tumor were detected by a hot spot of the tracer.
The detectability of FNH appears greater with HIDA (92%) than with CT or MRI (84%). The hot spot sign may be a useful tool when combined with the results of other imaging modalities in the diagnosis of FNH. Tanasescu et al. have described a characteristic triad in FNH: associated hypervascularization, normal uptake of colloids and accumulation of hepatobiliary tracer.
The peculiar pathology of FNH with fibrosis, hyperplastic hepatocytes and cholangiolar proliferation might explain this scintigraphy appearance. These findings suggest that liver cells involved in FNH maintained their normal uptake mechanisms but seem to have abnormal secretion and excretion functions.
Case
22 years old lady with history of lump in left side of neck, which is gradually increasing in size.
FNAC- Suspicion of Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Excision of left supraclavicular lymph node- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (Nodular sclerosis).
Spiral CT Chest- Mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
CT abdomen- Intrahepatic mass lesion in right lobe of liver (6.4*4.5 CMS), suspected FNH OR intrahepatic lymphoma.
Referred for Liver colloid scan and Hepatobiliary scan (HIDA Scan).
99mTc colloid liver scan-shows reduced to normal tracer uptake pattern in suspected right lobe lesion (figure 1)
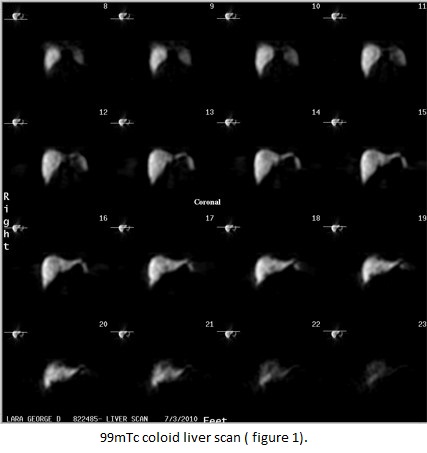
99mTc Mebrofenin (HIDA) scan- shows hypervascularity during the blood transport phase (figure 2) uptake phase is relatively normal, indicating that FNH hepatocytes do not have any difficulty in concentrating IDA agents. The fact that FNH tissues become increasingly visible on delayed images
(figure 3) clearly demonstrates that the hepatocytes or the bile canaliculi draining these hepatocytes are at fault, hence the slow clearance of IDA from the nodule favoring FNH in right lobe of liver.
Liver Biopsy- FNH
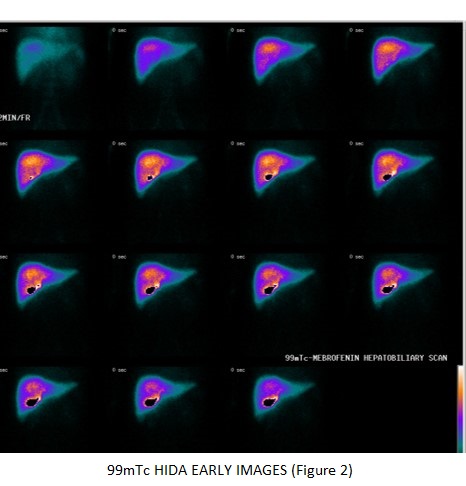
Hepatobiliary scintigraphy, that demonstrate hot spots in the region of the tumor, seem to be useful tool when combined with other imaging techniques in the diagnosis of FNH.