CASES OF THE WEEK - “Early Chronic pancreatitis diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)” by Dr Piyush Somani, Specialist Gastroenterologist, NMC Royal Hospital Sharjah
Early Chronic pancreatitis diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
A 33 years old male, non-alcoholic and non-smoker presented with history of recurrent episodes of mild upper abdominal pain with dyspepsia since few months. He was treated with proton pump inhibitors and prokinetics with no improvement.
On laboratory investigations, there was mildly elevated serum amylase. Ultrasound abdomen revealed fatty liver with normal pancreas. The patient had recurrent upper abdominal pain with undiagnosed etiology.
Patient underwent upper gastrointestinal endoscopy with Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS).
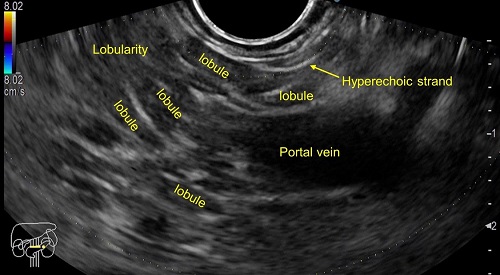
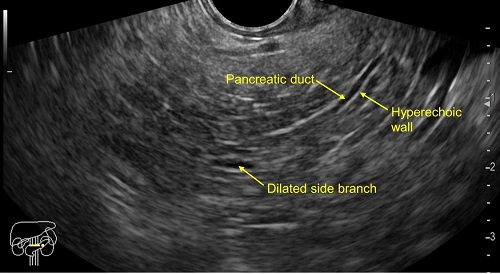
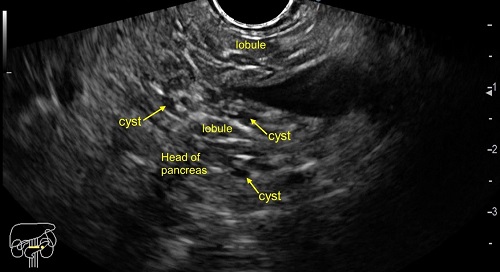
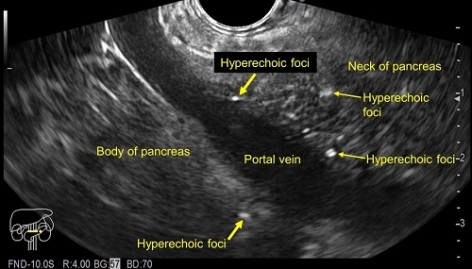
The EUS revealed features of early chronic pancreatitis (CP) like lobularity, hyperechoic strands, hyperechoic foci, few dilated pancreatic duct side branches, cysts and hyperechoic wall of main pancreatic duct.
The diagnosis of CP is based upon the demonstration of morphological and/or functional changes in the pancreas. Various imaging techniques such as transabdominal ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are utilized for assessment of the morphological changes in the pancreas.
However, these imaging techniques can diagnose advanced morphological changes only, and the diagnostic ability of these techniques to diagnose early and minimal CP is quite limited.
In view of close proximity of the transducer to the pancreas, EUS is considered the most sensitive imaging technique for diagnosing pancreatic disorders. EUS has been demonstrated to show subtle alterations in the pancreatic parenchymal and ductal structure even before traditional imaging and functional testing demonstrate any abnormality.
The diagnosis of CP by EUS is based upon the demonstration of ductal and parenchymal features, and a number of diagnostic criteria incorporating these EUS features have been proposed to diagnose CP.
Parenchymal criteria includes hyperechoic foci, lobularity, hyperechoic strands, cysts and calcifications. Ductal criteria includes main pancreatic duct dilatation, main pancreatic duct irregularity, main pancreatic duct hyperechoic wall and dilated side branches.
The higher the number of criteria, the more chances of chronic pancreatitis. Usually, more than 4-5 criteria is used to make diagnosis of CP in various studies.
A number of conditions such as aging, smoking, obesity, and chronic alcohol consumption may cause EUS changes similar to CP. Therefore, EUS findings should be interpreted in appropriate clinical context.
In summary, EUS is the most sensitive imaging modality for pancreas and should be performed for detecting any suspected pancreatic disorder based on laboratory tests or clinical suspicion.