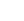CASES OF THE WEEK – “Additional benefit of bone spect-ct in investigating heel pain (a case of left foot achilles tendonitis)” by Dr ShekharShikare, HOD & Consultant, Nuclear Medicine
ADDITIONAL BENEFIT OF BONE SPECT-CT IN INVESTIGATING HEEL PAIN (A CASE OF LEFT FOOT ACHILLES TENDONITIS)
In diagnosing ankle and foot pain, clinical examination is a basic process and may provide accurate diagnosis in many cases. However, clinical examination is often limited, particularly in patients with vague and chronic pain. Imaging studies are effective for diagnosis and planning of surgical treatment. Currently, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most effective diagnostic imaging method in ankle and foot pain, with strengths such as high image resolution and excellent soft tissue contrast. In an expert consensus report, MRI was recommended as the most appropriate imaging method for ankle and foot pain when simple X-ray images are negative. However, clinical MRI is based on structural changes, and may have limitations when there are only subtle structural changes or when there are several coexistent lesions.
Bone scan and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) using 99mTc-labeled phosphonate agents can show increased bone metabolism or bone turnover in injured bones, which is also related to the joint inflammation and ligament/tendon injury as a secondary change. For detection of pathogenic lesions, changes in bone turnover are often complementary to structural changes. Thus, bone scan and SPECT have been demonstrated to be effective in diverse musculoskeletal disorders. Furthermore, SPECT/CT, a hybrid imaging method incorporating SPECT and computed tomography (CT), has the advantage that CT is utilized for lesion localization. In cases with ankle and foot pain, bone SPECT/CT is also expected to be effective and of an additive diagnostic value to MRI, because of their different imaging mechanism.
Case
56 years old lady complaining of dull ache specially when moving the left limb or joint and backache on and off since long. On examination-tenderness and mild swelling at the Achilles tendon region of left foot. Referred for Isotope bone scan
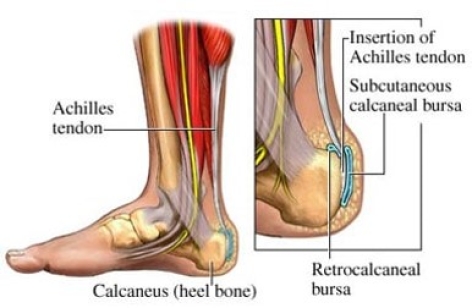
99mTc MDP bone scan
Blood pool phase of foot shows focal area of abnormal pooling of tracer in left calcaneum postero-superiorly (figure 1)
Bone phase of foot shows focal area of abnormal pooling of tracer seen in left calcaneum postero-superiorly (figure 1)
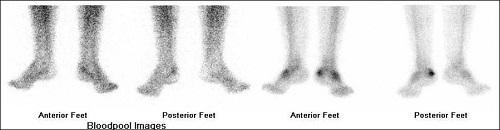
BONE SPECT-CT FUSED images of foot shows focal area of increased tracer uptakes at the insertion of Achilles tendon of left foot and underlying CT images (figure 3 & 4) shows dystrophic calcification at the insertion of LEFT tendo-achillis, favors Achillis tendonitis.
A hybrid imaging of SPECT/CT can provide high-resolution CT images for lesion localization, and enhanced diagnostic accuracy. The uptake on bone SPECT/CT was significantly associated with pain or pain relief after local injection of anesthetics.99mTc-MDP SPECT/CT results led to changes in treatment plan in 48–52% of patients, compared with MRI alone. The SPECT/CT could be suggested as an effective complementary imaging method for MRI in ankle and foot pain patients. SPECT/CT may be effective for improving diagnostic specificity in combination with MRI.
ACHILLES TENDONITIS
99mTc MDP bone scan (figure 1)
Blood pool phase of foot shows focal area of abnormal pooling of tracer in left calcaneum postero-superiorly.
Bone phase of foot shows focal area of abnormal pooling of tracer seen in left calcaneum postero-superiorly.
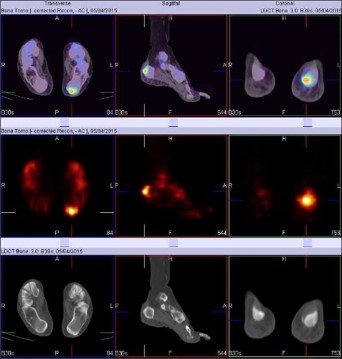
Figure 2 - BONE SPECT-CT FUSED images of foot shows focal area of increased tracer uptakes at the insertion of Achilles tendon of left foot favors ACHILLIS TENDINITS.
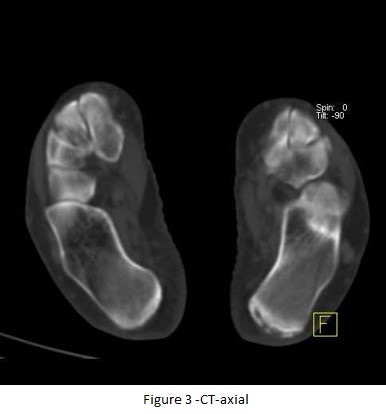
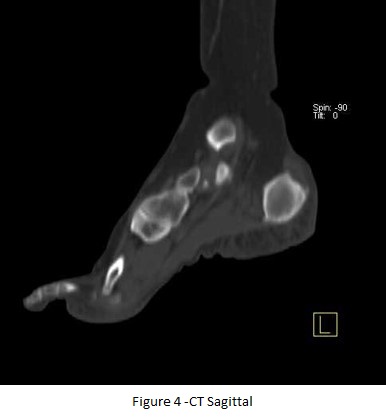
CT-axial (fig 2) & CT Sagittal images (fig 3) shows dystrophic calcification at the insertion of tendo-achillis (left).