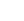Varicose Veins
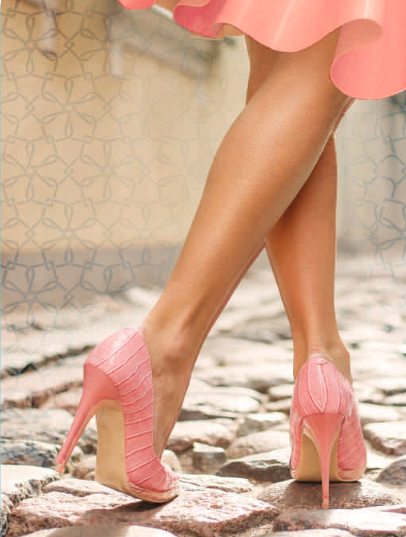

What are Varicose veins?
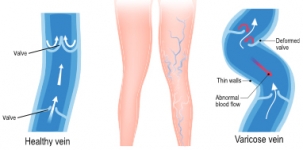
Varicose veins are swollen, enlarged veins that are clearly visible just under the surface of the skin.
In a healthy vein, blood flows smoothly to the heart. The blood is prevented from flowing backwards by a series of tiny valves that open and close to let blood through. If the valves weaken or are damaged, the blood can flow backwards and collect in the vein, eventually causing varicose veins.
Many factors can raise your risk for developing varicose veins, including family history, older age, female gender, pregnancy, obesity, prolonged standing or sitting, blood clots and prior trauma.
What are the symptoms of varicose veins?
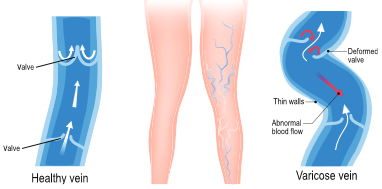
Varicose veins may not cause any pain. Signs you may have with varicose veins include:
- Veins that are dark purple or blue in color
- Veins that appear twisted and bulging; often like cords on your legs
- When painful signs and symptoms occur, they may include:
- An achy or heavy feeling in your legs
- Burning, throbbing, muscle cramping and swelling in your lower legs
- Worsened pain after sitting or standing for a long time
- Itching around one or more of your veins
- Bleeding from varicose veins
- A painful cord in the vein with red discoloration of the skin
- Color changes, hardening of the vein, inflammation of the skin or skin ulcers near your ankle, which can mean you have a serious form of vascular disease that requires medical attention
How to diagnose varicose veins?
To diagnose varicose veins, you will require a physical exam by your doctor, including looking at your legs while you’re standing to check for swelling.
You also will need an ultrasound test to see if the valves in your veins are functioning normally or if there’s any evidence of a blood clot. In this noninvasive test, a small hand-held device (transducer), about the size of a bar of soap, is held against your skin over the area of your body being examined. The transducer transmits images of the veins in your legs to a monitor, so your doctor can see them
What are the treatment options?
- Sclerotherapy
- Endovenous Laser Therapy(EVLT)
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)