Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes overview
Diabetes is a condition in which blood sugar is high. Body needs some glucose in the blood for energy at a range of 80-120mg/dl. But above that range; it is not good for health.
Role of insulin in the body:
Insulin is a hormone secreted by pancreas which is necessary for the body to transport the glucose from the blood into cells in our body eg. Muscle cells, where it is used as energy for the body. Acting like key, insulin unlocks the cell so glucose can pass into it. There, most of the glucose is used for energy right away. Insulin “opens” the cells, like a key, and makes glucose pass into the cells in our body
Diabetes develops when there is shortage of insulin or the available insulin does not work properly on the cells causing excess of glucose in the blood.
Types of diabetes.
Type 1 or Insulin dependent Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
In this type of DM pancreas produces little or no insulin and definitely needs insulin therapy for survival. It can develop at any age but most common in children teenagers or young adults. There is absolute insulin deficiency in Type 1 DM.
Diabetes develops when glucose can’t enter the body’s cells to be used as fuel. This happens because either...
There is nokey (Insulin) to unlock the door to the cells, as in Type 1 Diabetes
Type 2 or Non Insulin dependent Diabetes mellitus(DM)
This is the most common diabetes. In this, the insulin is not enough, or the insulin has difficulty to unlock the door of the cells for the glucose to get into the cells resulting in surplus glucose in blood. This is called insulin resistance which is predominant feature in Type2 DM.
or the key (Insulin) is unabe to unlock the door properly and/ or the key (Insulin) is there but the lock doesn’t work properly as in Type 2 Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes High blood sugar that starts or first diagnosed in pregnancy. Pregnancy hormones blocks insulin from doing its job which causes blood glucose to rise.
Are you at risk of diabetes?
Your risk of diabetes is high if you have any of these:
- Age above 45 years
- Ethnic background (South Asians, Middle Eastern, black African, Hispanic/Latino American)
- Prediabetes
- High blood pressure or history of heart attack
- Low HDL (good cholesterol) or high triglycerides
- Overweight or obese
- Family History of diabetes (Parent, brother, sister)
- History of gestational diabetes
- History of polycystic ovary syndrome
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
If you have more than one of these symptoms, you may want to ask your doctor to test your blood sugar
- Blurred vision
- Unusual thirst
- Frequent urination
- Slow-healing cuts
- Unexplained tiredness
- Rapid weight loss (Type 1 diabetes)
- Erectile dysfunction
- Numbness or tingling in hands or feet
Symptoms may occur rapidly with Type 1 diabetes; however, with Type 2 diabetes the onset is more insidious and may not be noticed.
How is diabetes diagnosed?
The diagnosis of diabetes is made by a simple blood test measuring your blood glucose level.
Usually these tests are repeated on a subsequent day to confirm the diagnosis.
Blood sugar levels in diagnosing diabetes
The following table lays out criteria for diagnoses of diabetes and prediabetes
| Plasma Glucose test | Normal | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random | N/A | N/A | 11.1 mmol/l or more 200 mg/dl or more |
| Fasting | Below 5.8 mmol/l Below 100 mg/dl |
5.8 to 6.9 mmlol/l 100 to 125 mg/dl |
7.0 mmol/l or more 126 mg/dl or more |
| 2 Hr post-prandial | Below 7.8 mmol/l Below 140 mg/dl |
7.8 to 11.0 mmlol/l 140 to 199 mg/dl |
11.1 mmol/l or more 200 mg/dl or more |
Hypoglycemia “Low blood sugar”
Hypoglycemia is when the glucose level in the blood (‘blood sugar level’) drops below the normal range due to too little food or too much insulin, diabetes pills or being more active than usual
Below normal is when it is less than 3.8 mmol/L (70 mg/dl).
Low blood sugar treatment
If you feel your blood sugar going low, you should treat it as soon as possible. If untreated symptoms can become more severe, and you may become unconscious or have sever seizures.
Hypoglycemia can be corrected by taking something sweet to drink or eat, such as:
- ½ cup of fresh or sweetened fruit juice
- ½ cup of regular soda
- 4 teaspoons of sugar
- One tablespoon of honey
- 3 Dates
- 3 Glucose tablets
If you will not be eating a proper meal within the next hour, you should eat some carbohydrate (starchy) food like a cereal bar or a sandwich. This will make sure that your blood sugar does not go low again.
To control your blood sugar levels:
Your doctor might prescribe for you diabetes medication, the most important thing you can do is to take it regularly as prescribed. In addition, doctor will advise you on healthy lifestyle, weight management & exercise.
- For the medications to be effective:
- You should take them in the correct way at the right time.
- Know the names and doses of your medications and its instructions
- Don’t Skip any medication which is prescribed.
- Don’t self-prescribe or modify the doses without expert consultation.
Medications
Type 1 Diabetes: the choice is only insulin injections.
Type 2 diabetes: the treatment includes life style modifications, oral medications and/or insulin depending on the case.
Low Blood Sugar Symptoms

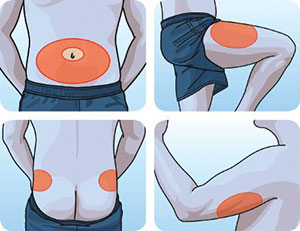
Insulin Injection Sites
The main areas for insulin injections are the abdomen, thighs, and the back of the upper arms. (As there is enough fat under the skin)
- The abdomen is used the most. It’s easy to reach and the insulin is absorbed at a more consistent rate from shot to shot.
- Make sure that you don’t inject too close to any scar.
- Each injection site should move about a finger width or (2cms.) away from your last shot and each time you should rotate.
- If you inject in the arm, use only the outer back area of the upper arm.
- When you inject in the thigh, use only the top and the outside area. Stay away from the inner thighs; rubbing between the legs can make the injection site sore.
- If you inject in the abdomen, don’t do it too near to the navel.
- If the skin around an injection site(s) begins to look lumpy due to repeated shots in the same spot, stop using that site and consult your doctor/educator
What are the complications of diabetes?
If Diabetes is not treated, it can harm different parts of the body. The complications include:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Kidney damage (nephropathy)
- Eye damage (retinopathy)
- Foot damage
- Hearing impairment
- Alzheimer’s disease
To reduce your risk of complications:
- Seek regular consultation with your doctor every 3-6 month
- Quit smoking
- Check annually your eyes by an ophthalmologist.
- Take care of your feet; seek expert consultation with a podiatrist if needed.
- Keep track of your blood glucose, blood pressure, cholesterol at regular intervals. (ABCs of Diabetes Care)
- A - A1C - less tham 7 % (every 3-6 months)
(The A1C Test shows you what your blood glucose has been over the last three months. The A1C goal for many people is below 7)
- B- Blood pressure -130/80mmHg (every doctor’s visit)
- C - Cholesterol (every 6 months -1 year)
- LDL (bad cholesterol) – less than 100 mg/dl or less than 2.6mmol/L
- HDL (good cholesterol) > 40 mg/dl or> 0.9 mmol/L for men and greater than 50mg/dl for women
- Triglyceride less than 150 mg/dl or 1.8 mmol/l
Life style modification
Diet and exercise plays a key role in managing diabetes. Maintaining an ideal body weight is very important. Excess weight always causes poor control of blood sugar.
Eat healthy:
There are three main types of food- carbohydrate, proteins& fat. A healthy meal will have all these. However, you need to control the amount of carbs as it can raise your blood sugar faster than the other two. Therefore, a healthy plate will have
¼ protein, ¼ carbs and ½ vegetables.
Being Active:
Exercising for 30 – 45 minutes or more a day is a good goal for diabetic patient.
If you are short on even 10 minutes of exercise 2 to 3 times a day can be good for you.
Make physical activity and exercise a part of your daily routine, for 30 min/day for 5 days.
Benefits of Exercise include:
- Lower blood sugar
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Weight control
- Lower blood pressure and cholesterol
- Prevent heart disease
- Develop stronger
- Reduce stress and improve complete well being
Exercise should be fun
- Find an exercise that you enjoy to do.
- Find a friend or family member to get you going.
- Start with easy exercises like brisk walking, cycling, swimming etc.
Tips to get started
- Consult with your doctor before you start.
- Start with brisk walk, jogging, aerobic exercise
- Start on a slow pace. Start your exercise slowly.
- Check your feet before and after exercise.
- Exercising 1 to 2 hours after a meal is beneficial as blood sugar is high during that time.
- Avoid exercise soon after a heavy meal.
Here are some simple steps to start with
- Take the stairs not the elevator.
- Make your coffee break a walking break instead.
- Park your car a few blocks away from where you are going to walk.
- Any time you have more than 10 minutes to wait, take a walk.
Precautions:
- Always talk to your doctor before start an exercise schedule.
- Monitor your blood sugar before and after you are active – especially if you are type 1 DM.
- Drink extra fluids before, during and after your exercise.
- Learn symptoms of low blood sugar and how to treat it.
- Eat a high sugar candy or snack blood sugar is less than 100mg/dl.
- Wear comfortable shoes and clothes and wear ID showing that you are diabetic.
- Inject insulin into abdomen (Less active site) before exercising.
Do not exercise:
- If blood sugar is less than 100mg/dl or more than 240 mg / dl
- If You feel dizzy; have pain or shortness of breath
- Right before and after a meal
Carbs requirement for activity: (only for moderate & heavy activity)
Moderate activity: One extra serving of carbohydrate (15 grams of carb) - A snack like 1 slice of bread, 3 crackers, 1 cup skimmed milk and 1 apple.
Heavy activity: Two extra serving of carb containing food (30 grams of carbohydrate).
| Light Activity | Moderate Activity | Heavy Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Strolling | Scrubbinng floor | Fast cycling |
| Dressing | Bowling | Karate |
| Undressing | Gardening | Basketball |
| Preparing food | Golfing | Swimming |
| Sweeping floors | Walking fast | Tennis singles |
| Dusting furniture | Tennis | Running |
| Fishing | Volley ball Dancing |
Running |
Diabetes Management at NMC Royal Hospital Sharjah
- We follow a structured plan, which is evidence based and personalized to suit our individual patient’s needs.
Our qualified Team of Endocrinologists, Diabetes educators & dieticians can help you with:
- Prescribing medications that is best suited for each patient
- Providing Detailed explanations of the side effects and contraindications of the medicine
- Counselling with regards to lifestyle modifications, Diabetes monitoring & diet.