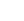Sigmoidoscopy
What is Flexible Sigmoidoscopy?
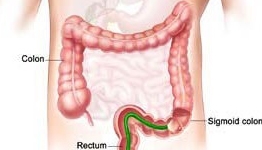
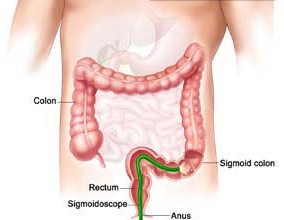
Flexible Sigmoidoscopy lets your doctor examine the lining of the rectum and a portion of the colon (large intestine) by inserting a flexible tube about the thickness of your finger into the anus and slowly advancing it into the rectum and lower part of the colon.
What preparation is required?
Your doctor will tell you what cleansing routine to use. In general, preparation consists of one or two enemas prior to the procedure but could include laxatives or dietary modifications as well. However, in some circumstances your doctor might advise you to have a special preparation, it is essential that the rectum and lower colon must be empty prior to the procedure. For an accurate assessment, it’s important to follow your doctor’s instruction carefully.
Should I continue my current medications?
Most medications can be continued as usual. Inform your doctor about medications that you’re taking – particularly aspirin products or anticoagulants (blood thinners such as warfarin or heparin), or clopidogrel, as well as any allergies you may have to medications.
What can I expect during Flexible Sigmoidoscopy?
Flexible sigmoidoscopy is usually well-tolerated. You might experience a feeling of pressure, bloating or cramping during the procedure. You will lie on your side while your doctor advances the sigmoidoscope through the rectum and colon. As your doctor withdraws the instrument, your doctor will carefully examine the lining of the intestine.
What if the Flexible Sigmoidoscopy finds something abnormal?
If your doctor sees an area that needs further evaluation, your doctor might take a biopsy (tissue sample). Obtaining a biopsy does not cause any pain or discomfort. Biopsies are used to identify many conditions, and your doctor might order one even if he or she doesn’t suspect cancer.
If your doctor finds polyps, he or she might take a biopsy of them as well. Polyps, which are growths from the lining of the colon, vary in size and types. Polyps known as “hyperplastic” might not require removal, but benign polyps known as “adenomas” have a small risk of becoming cancerous. Your doctor will likely ask you to have a colonoscopy (a complete examination of the colon) to remove any large polyps or any small adenomas.
What happens after a Flexible Sigmoidoscopy?
Your doctor will explain the result to you when the procedure is done. You might feel bloating or some mild cramping because of the air that was passed into the colon during the examination. This will disappear quickly when you pass gas. You should be able to eat and resume your normal activities after leaving your doctor’s office or the hospital, according to your doctor’s instructions.
Important Reminder:
The preceding information is intended only to provide general information and not as a definitive basis for diagnosis or treatment in any particular case. It is very important that you consult your doctor about your specific condition.