Nailfold Video Capillaroscopy
Main indications for NVC:
- Evaluation of patients with Raynaud’s Phenomenon.(RP)
- Monitoring the transition from primary to secondary RP.
- Early diagnosis of Scleroderma (SSc).
- Differential diagnosis of SSc-related conditions.
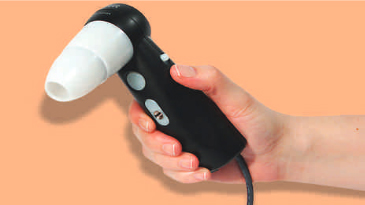
Videocapillaroscope consists of:
The combination of a microscope with a large magnification lens, coupled with a digital camera. NVC is a simple painless procedure. A drop of oil immersion is placed on the cuticle of the finger to be evaluated and the capillaries at the nailfold are visualized. Nailfold region of eight fingers (excluding thumbs) should be examined.
What is Nailfold Video Capillaroscopy (NVC)?
(NVC) is a non-invasive, reliable and reproducible diagnostic procedure to study the microcirculation at the nailfold. It represents the best method to detect and analyse microvascular abnormalities in autoimmune rheumatic diseases, particularly Scleroderma thus helping in early diagnosis.
Why is it considered a revolution in rheumatology?
- Firstly, it is the most reliable way to distinguish between Primary Raynaud’s phenomenon (not related to any clinical condition) and secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon (related to connective tissue disease )
- Secondly, NVC helps in early diagnosis of Scleroderma (SSc) and assists in predicting its associated medical complications as investigators have found correlation between severity of blood vessels abnormalities and disease complications g. Digital ulceration, Pulmonary hypertension and interstitial lung disease.
What is Raynaud’s phenomenon?
Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP) is the change of colour of fingers and toes due to disorder of the blood vessels, induced by exposure to cold and stress.
During an attack, the fingers and toes can change colours. They may go from white to blue to red. All three colour changes are observed in classic Raynaud’s. However, not all patients see all of the mentioned colour changes in all episodes.
Affected extremities my be felt cold and numb due to lack of blood flow. As the attack ends and blood flow restores, patient may experience throbbing and tingling of the affected hands and feet.
What is Scleroderma (SSc)?
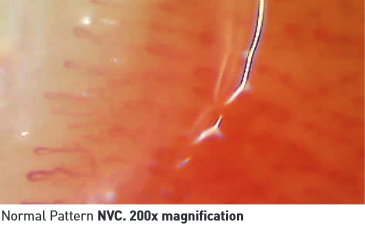
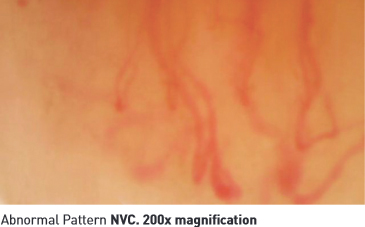
Also known as systemic sclerosis, is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease characterised by chronic hardening and shrinking of the connective tissues of any organ of the body, including the skin, heart, esophagus, kidney, or lung. The skin may be thickened, hard, and rigid, and pigmented patches may occur.
Scleroderma patients can present with skin tightening, joint pain and/or swelling, muscle pain and/or weakness, cough or shortness of breath, heartburn due to acid reflux and high blood pressure particularly when they take steroids.